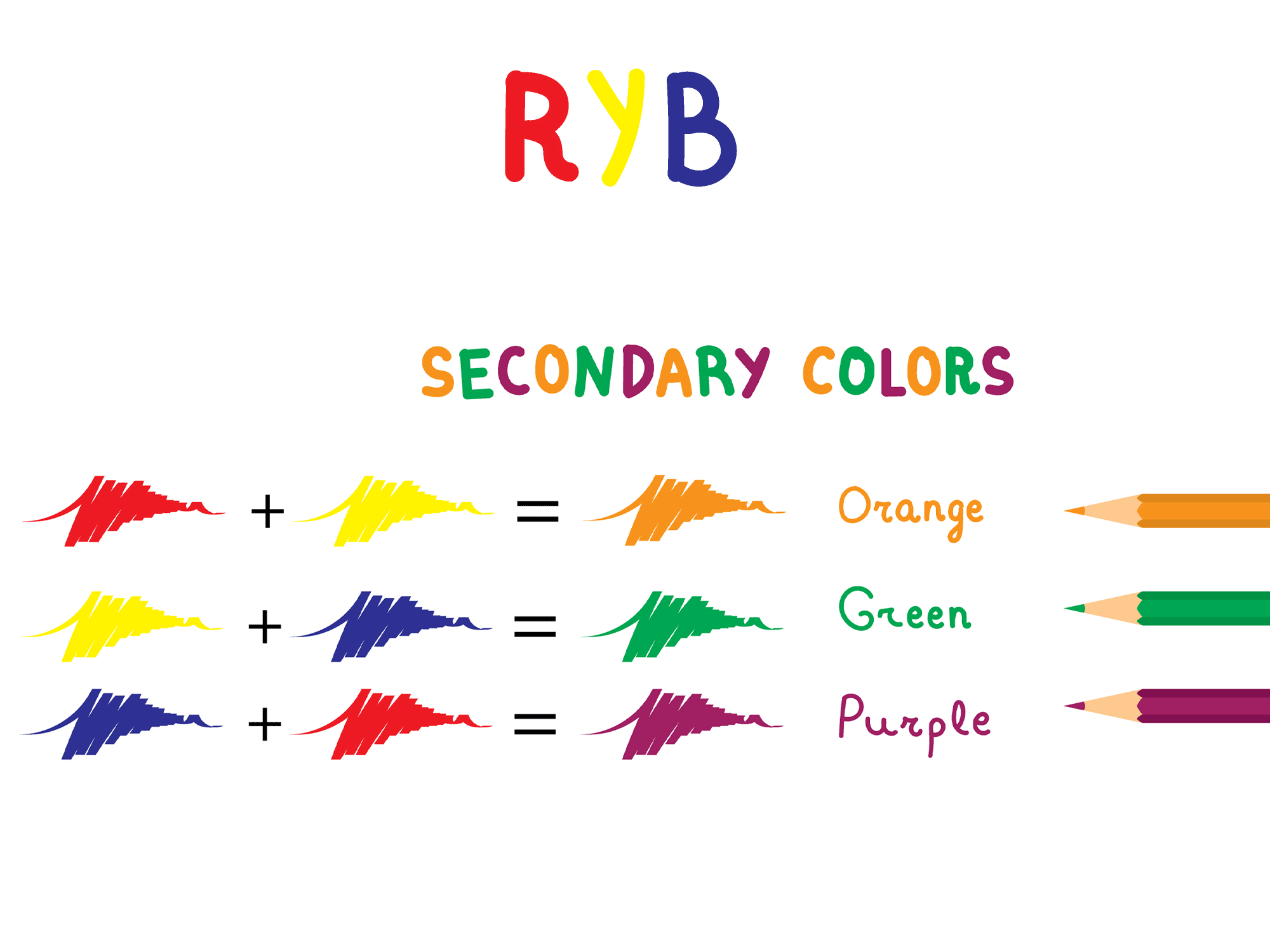Colors shape the way we see the world, adding depth, emotion, and vibrance to our lives. But have you ever wondered about the role that secondary colors play in the grand spectrum of hues? Secondary colors are pivotal in art, design, and everyday aesthetics, bridging the gap between primary shades and creating harmonies that resonate with the human eye. Understanding their formation and application can open up a world of creative possibilities, whether you’re an artist, designer, or simply someone who loves color.
At its core, the concept of secondary colors is deeply rooted in the color wheel, a tool that has guided creatives for centuries. These hues are not random; they are meticulously formed by blending two primary colors in equal parts. The result? A spectrum of hues that are just as vivid and essential as their primary counterparts. But secondary colors aren't limited to just visual appeal—they carry emotional weights, cultural significance, and practical applications across industries.
In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into what colors are secondary colors, how they are formed, and the many ways they are used in various fields. We’ll also address frequently asked questions and provide insights into how secondary colors can transform your creative projects. By the end of this guide, you’ll not only understand the technicalities behind these hues but also gain the confidence to use them effectively in your own work. Let’s begin our colorful journey!
Read also:Unveiling The Vibrant World Of Manheim Pennsylvania Auction Events
Table of Contents
- What Are Secondary Colors?
- How Are Secondary Colors Created?
- What Are the Three Secondary Colors?
- Why Are Secondary Colors Important?
- Secondary Colors in Art
- Secondary Colors in Design
- Secondary Colors in Nature
- How Do Secondary Colors Influence Mood?
- What Is the Difference Between Primary and Secondary Colors?
- How Are Secondary Colors Used in Marketing?
- What Are Tertiary Colors?
- Secondary Colors in Culture and Symbolism
- Tips for Using Secondary Colors in Art and Design
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Are Secondary Colors?
Secondary colors are hues that are formed by mixing two primary colors in equal proportions. In the traditional color wheel, the primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. When these are combined, they create the three secondary colors: orange, green, and purple. These colors form an essential part of the standard color wheel and play a key role in color theory.
Here’s a quick breakdown of how they are created:
- Orange: A mix of red and yellow.
- Green: A mix of blue and yellow.
- Purple: A mix of red and blue.
These colors are called “secondary” because they are derived from the primary colors rather than existing independently. They are equally vibrant and versatile, serving as the foundation for more complex hues like tertiary colors (which we’ll touch on later in the article).
How Are Secondary Colors Created?
Creating secondary colors is a straightforward process, but achieving the perfect blend requires some precision. The idea is simple: combine two primary colors in equal parts. However, the type of medium you use—whether paint, digital software, or light—can influence the final result.
What Happens When You Mix Primary Colors?
When you mix two primary colors, their wavelengths interact to form a new color. For example:
- Mixing red and yellow produces orange, a warm and energetic hue.
- Mixing blue and yellow results in green, a color often associated with nature and balance.
- Mixing red and blue creates purple, often linked to luxury and creativity.
Does the Ratio Matter?
Absolutely! The final shade of the secondary color depends on the ratio of the primary colors used. For instance, adding more red than yellow when mixing for orange will result in a reddish-orange shade. Similarly, adjusting the proportions of blue and yellow can yield various shades of green, from lime to teal.
Read also:Gossip Slots Casino Your Ultimate Guide To Winning Big
What Are the Three Secondary Colors?
The three universally recognized secondary colors are:
- Orange: Created by mixing red and yellow, orange is a warm and vibrant hue.
- Green: Formed by combining blue and yellow, green symbolizes nature, growth, and harmony.
- Purple: A blend of red and blue, purple evokes creativity, luxury, and mystery.
These colors are fundamental to the color wheel and serve as stepping stones for creating tertiary colors and beyond.
Why Are Secondary Colors Important?
Secondary colors are vital for several reasons:
- They expand the range of hues available for artistic and design purposes.
- They add depth and complexity to visual compositions.
- They help create harmonious color schemes, such as complementary or analogous palettes.
Without secondary colors, the world of design and art would be far less vibrant and dynamic. They are essential for creating a balanced and visually appealing aesthetic.
Secondary Colors in Art
Artists have long relied on secondary colors to evoke emotion, contrast, and balance in their work. These colors are often used to create depth and dimension, making compositions more engaging.
How Are Secondary Colors Used in Paintings?
In paintings, secondary colors are used to:
- Create shadows and highlights.
- Balance warm and cool tones.
- Draw attention to focal points.
For instance, an artist might use green to create a serene landscape or purple to evoke a sense of mystery.
Secondary Colors in Design
In design, secondary colors are crucial for creating visually appealing layouts and interfaces. They are often used in branding, web design, and interior design to convey specific emotions and messages.
Why Are Secondary Colors Popular in Branding?
Brands use secondary colors to:
- Stand out from competitors.
- Create a unique identity.
- Appeal to target audiences.
For example, a company might use orange to convey energy and enthusiasm, while green might be chosen to represent eco-friendliness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary colors?
Primary colors are red, blue, and yellow. They cannot be created by mixing other colors and serve as the foundation for secondary and tertiary colors.
Can secondary colors be mixed to create tertiary colors?
Yes, mixing a secondary color with a primary color produces tertiary colors. For example, mixing orange and yellow creates yellow-orange.
How do secondary colors affect mood?
Secondary colors can evoke a range of emotions. For instance, orange is uplifting, green is calming, and purple is inspiring.
Are secondary colors used in digital design?
Absolutely! Secondary colors are widely used in digital design for UI/UX layouts, web pages, and digital illustrations.
What’s the difference between additive and subtractive color mixing?
Additive mixing involves light (e.g., RGB), while subtractive mixing involves pigments (e.g., paint or ink).
Can secondary colors be customized?
Yes, you can adjust the ratios of the primary colors to create unique shades of secondary colors.
Conclusion
Secondary colors are more than just a mix of primary hues; they are a gateway to endless creative possibilities. From art and design to branding and beyond, these colors play a pivotal role in shaping our visual and emotional experiences. Whether you’re a seasoned designer or someone exploring the world of color for the first time, understanding what colors are secondary colors can help you unlock new levels of creativity. So, grab your palette and start experimenting—you’ll be amazed at what you can create!