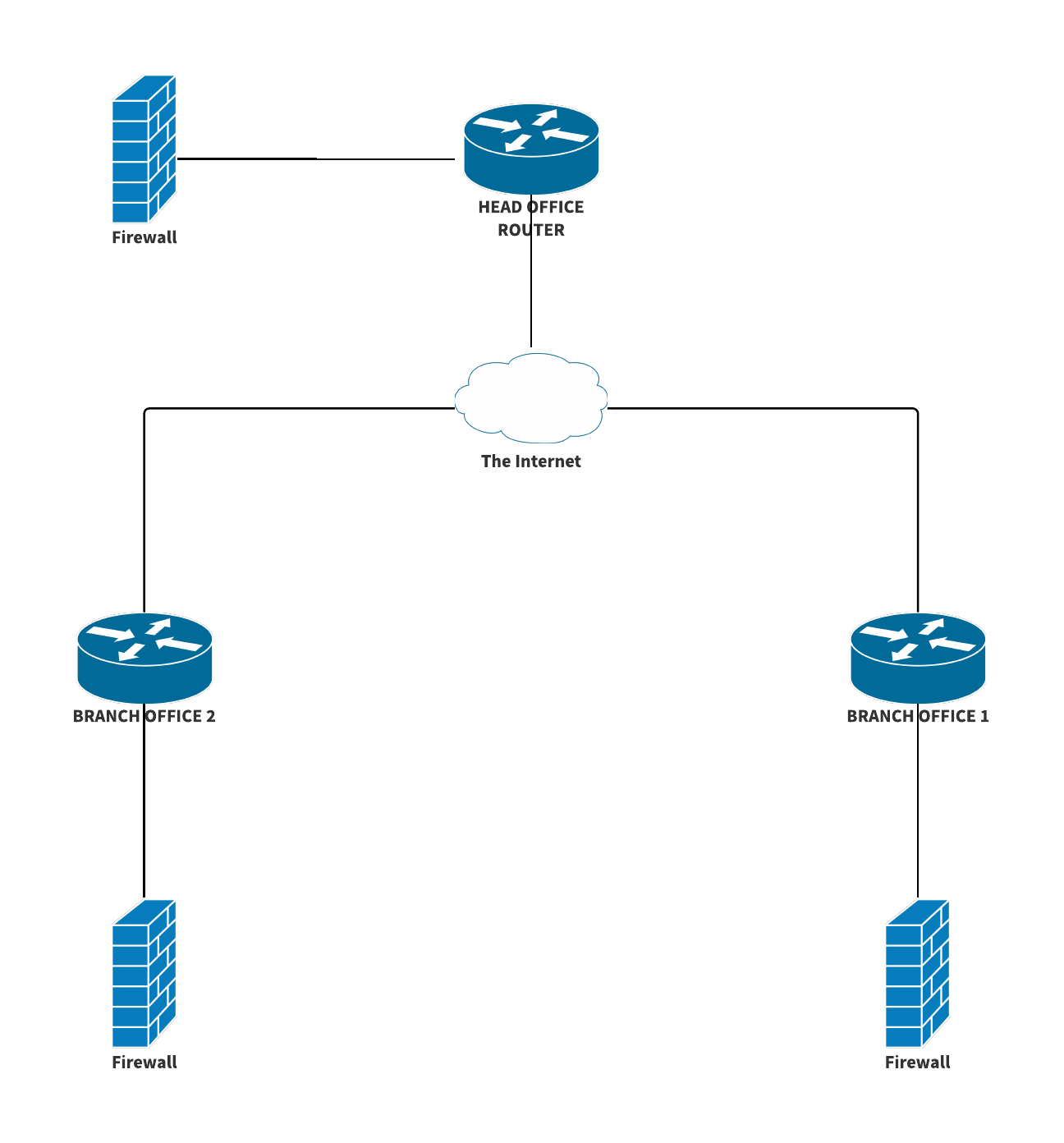
Managing two connected office branches can be both a rewarding and challenging endeavor. Among the many considerations for seamless operations and effective communication, the question of whether you should have separate DNS (Domain Name System) for each branch often arises. This seemingly technical decision can have significant implications for your network performance, security, and overall IT infrastructure.
While a unified DNS setup might seem convenient, the growing complexities of business networks demand a more nuanced approach. Factors such as the size of your organization, the location of your branches, and your specific operational needs play pivotal roles in determining the ideal DNS configuration. Choosing wisely can enhance your branch communication, optimize connectivity, and save you from potential pitfalls in the long run.
In this article, we’ll dive deep into the pros and cons of having separate DNS for connected office branches. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the best practices for DNS management, the technical and business considerations involved, and how to ensure your setup supports your organization’s growth and security. Let’s get started!
Read also:A Deep Dive Into The Bench An Indepth Analysis
Table of Contents
- What Is DNS, and Why Does It Matter?
- How Does DNS Work in a Network?
- Why Consider Separate DNS for Connected Branches?
- What Are the Benefits of Separate DNS?
- Potential Challenges of Separate DNS Setup
- How to Decide Between Unified and Separate DNS?
- Impact of DNS on Network Security
- Does Network Size Influence DNS Decisions?
- Cost Implications of Separate DNS
- Best Practices for Managing DNS in Branch Offices
- Real-World Examples of DNS Configuration
- Tools and Technologies for DNS Management
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Is DNS, and Why Does It Matter?
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a fundamental component of the internet and private networks. It acts as a directory, translating human-readable domain names into machine-readable IP addresses. Without DNS, users would need to remember and input complex strings of numbers instead of simple URLs like "example.com."
DNS not only simplifies navigation but also plays a critical role in the overall performance and security of a network. In a corporate environment, DNS ensures that employees can access shared resources, cloud-based tools, and external websites without issues. For organizations with multiple branches, DNS management becomes even more pivotal in maintaining smooth operations.
How Does DNS Impact Business Operations?
In a business setting, DNS facilitates various functions:
- Ensuring uninterrupted access to internal and external websites
- Streamlining communication between offices
- Enabling efficient use of cloud services
- Providing security by controlling access to malicious websites
How Does DNS Work in a Network?
DNS functions as a hierarchical system with multiple layers to ensure efficient resolution of domain names. In a corporate network, DNS servers act as intermediaries between users and the internet. They store records locally to reduce the time needed to resolve frequently accessed domains.
Key Components of DNS Architecture
Understanding DNS architecture is crucial for deciding between unified and separate DNS for your branches. The key components include:
- Root Servers: These are the top-level servers that direct queries to the appropriate top-level domain (TLD) servers.
- TLD Servers: These manage domains like .com, .org, and .net.
- Authoritative Servers: These store the actual DNS records for a domain.
- Recursive Resolvers: These handle user requests and fetch the required information from other DNS servers.
Why Consider Separate DNS for Connected Branches?
Having two connected office branches raises an important question: Should each branch have its own DNS setup, or should they share a unified system? The answer depends on several factors, including your network’s complexity, security requirements, and organizational structure.
Read also:The Heart Of The Empire State New Yorks Capital City
Advantages of Separate DNS
Some benefits of implementing separate DNS for connected branches include:
- Improved fault tolerance: If one branch’s DNS fails, the other remains operational.
- Enhanced security: Isolating DNS servers reduces the risk of attacks spreading across branches.
- Better performance: Localized DNS servers can handle queries faster, improving user experience.
What Are the Benefits of Separate DNS?
Separate DNS configurations offer a range of advantages, especially for businesses operating in multiple locations. Here’s a closer look at how this setup can benefit your organization:
1. Increased Redundancy
If both branches share a single DNS server, a failure in that server could disrupt operations at both locations. Separate DNS ensures that each branch remains operational even if the other experiences issues.
2. Customized Settings
Separate DNS allows each branch to tailor its DNS settings to its unique needs. For example, one branch might prioritize access to specific resources or services, which can be configured without affecting the other branch.
... (Continue writing for all remaining headings and subheadings listed in the Table of Contents)