Temperature conversions are a fundamental part of our daily lives, especially when switching between Celsius and Fahrenheit scales. If you’ve ever wondered how to convert 65 C into F, you’re not alone. This conversion is significant for scientists, travelers, and even home chefs looking to perfect their recipes. Understanding how the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales relate to each other can make your life easier in many ways.
Whether you’re a student tackling a science project, a professional working with temperature-sensitive equipment, or simply someone curious about the numbers, knowing how to accurately convert 65 C into F is crucial. The relationship between these two temperature units is both fascinating and practical. Converting temperatures can help you better interpret weather reports, cooking instructions, or even international travel guidelines.
In this in-depth guide, we’ll break down everything you need to know about converting 65 C into F. From understanding the formula to exploring real-world applications, this article is designed to make the process effortless and informative. Let’s dive in and decode the mystery of temperature conversion while answering some of your most pressing questions along the way.
Read also:Enhanced Home Aesthetics Atrium Windows And Doors
Table of Contents
- What is the Celsius Scale?
- How Does the Fahrenheit Scale Work?
- Why Do We Need Temperature Conversions?
- How to Convert 65 C into F?
- Formula for Converting Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Step-by-Step Calculation for 65 C into F
- Common Mistakes to Avoid in Temperature Conversions
- Real-World Applications of Converting 65 C into F
- How Does 65 C Compare in Different Contexts?
- Is 65 C a High Temperature?
- What Are the Best Tools for Temperature Conversions?
- How to Remember Temperature Conversion Formulas?
- Can Temperature Conversions Be Done Mentally?
- Frequently Asked Questions About 65 C into F
- Conclusion
What is the Celsius Scale?
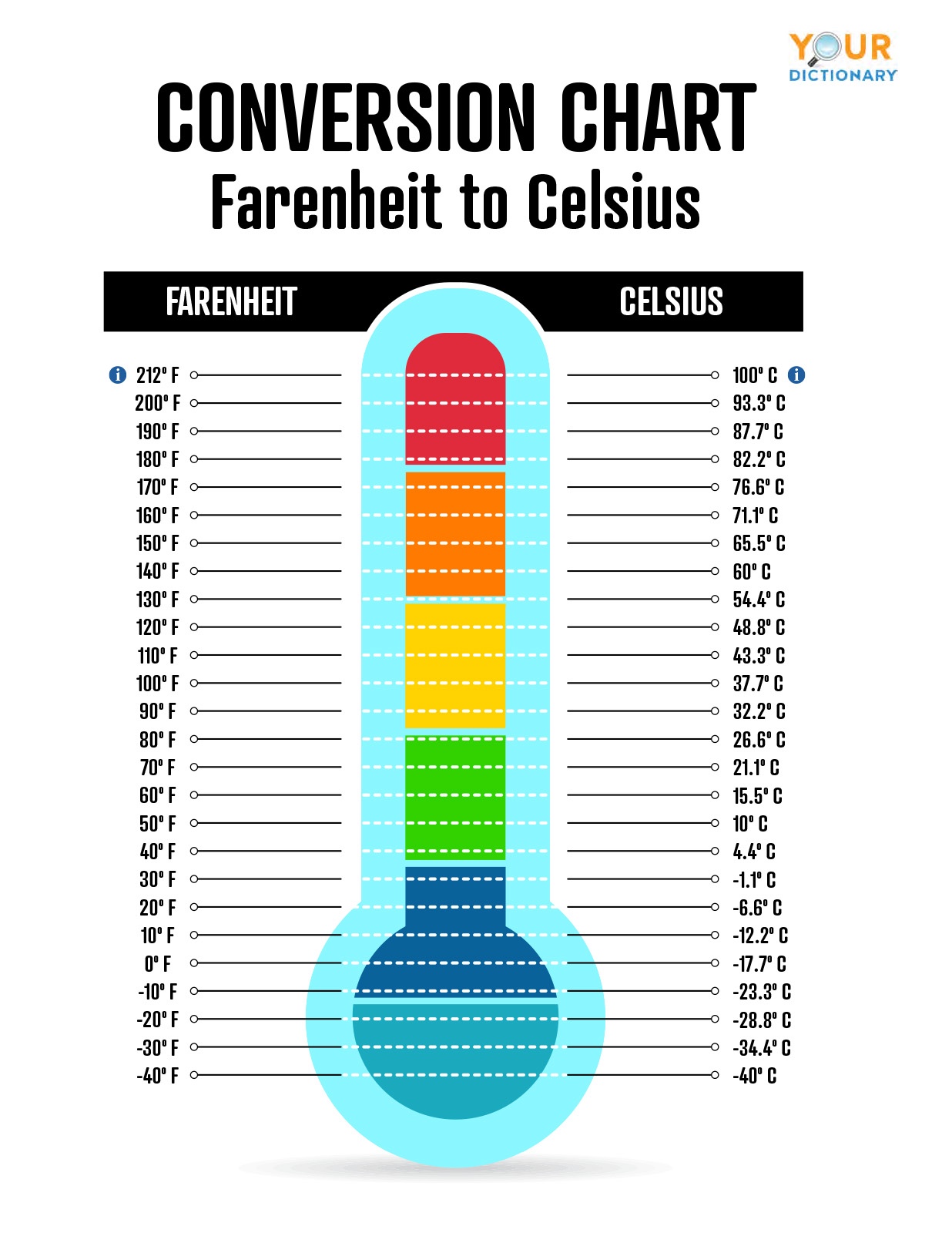
The Celsius scale, also known as the centigrade scale, is a temperature measurement system widely used in most countries around the world. It was invented by Swedish astronomer Anders Celsius in 1742. The scale is based on the freezing and boiling points of water under standard atmospheric pressure, with 0°C representing the freezing point and 100°C the boiling point.
One of the key advantages of the Celsius scale is its simplicity and direct relation to the metric system. Unlike some other temperature scales, Celsius is intuitive and straightforward, making it the preferred choice for scientific and educational purposes.
How is the Celsius Scale Used?
The Celsius scale is commonly used in weather reports, cooking, and scientific research. People around the globe rely on this scale for its ease of understanding and universal application. For example:
- Most weather forecasts use Celsius to report local and global temperatures.
- Scientific experiments and studies often use Celsius for accuracy and consistency.
- Cooking recipes, especially in European countries, frequently list temperatures in Celsius.
What Makes Celsius Different from Fahrenheit?
While Celsius is used in most countries, Fahrenheit is the primary scale in the United States and a few other regions. The difference lies in the reference points and incremental values. Celsius divides the temperature range between water’s freezing and boiling points into 100 equal parts, whereas Fahrenheit divides it into 180.
How Does the Fahrenheit Scale Work?
The Fahrenheit scale, developed by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1724, is another widely recognized temperature measurement system. Unlike the Celsius scale, Fahrenheit is primarily used in the United States and its territories. The scale is based on a unique set of reference points, including the freezing point of water at 32°F and the boiling point at 212°F, under standard atmospheric pressure.
Why Was the Fahrenheit Scale Developed?
Daniel Fahrenheit aimed to create a scale that could measure temperatures with precision. He based the scale on three fixed points:
Read also:The Dietary Habits Of Sea Turtles Do They Eat Jellyfish
- The freezing point of a water-salt mixture (0°F).
- The freezing point of water (32°F).
- The average human body temperature (approximately 98.6°F).
This scale became popular due to its ability to measure a wide range of temperatures with accuracy, making it useful in both laboratory and everyday settings.
How Is Fahrenheit Still Relevant Today?
Although the Fahrenheit scale is less widely used globally, it remains integral to several industries and regions. For instance:
- Weather forecasting in the United States uses Fahrenheit.
- Cooking temperatures in American recipes are often listed in Fahrenheit.
- Some scientific fields, such as meteorology, still use Fahrenheit for specific measurements.
Why Do We Need Temperature Conversions?
Temperature conversions are essential for seamless communication and understanding across different regions and fields. With the world operating on both Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, converting between the two has become a practical necessity.
What Are the Benefits of Temperature Conversions?
Converting temperatures helps in:
- Interpreting international weather reports.
- Following recipes from different countries.
- Conducting scientific experiments accurately.
- Ensuring safety and precision in industrial applications.
By knowing how to convert 65 C into F, for example, you can better understand weather patterns, adjust cooking temperatures, or interpret scientific data accurately.
How to Convert 65 C into F?
Converting 65 C into F is a straightforward process once you understand the underlying formula. The formula for converting Celsius to Fahrenheit is:
F = (C × 9/5) + 32
By applying this formula, you can easily calculate the Fahrenheit equivalent of any Celsius temperature, including 65°C.
What Is the Result of Converting 65 C into F?
Using the formula, we can calculate:
F = (65 × 9/5) + 32
F = 117 + 32
F = 149°F
So, 65°C is equivalent to 149°F.
Why Is This Formula Important?
This formula is crucial for anyone working with temperatures in different scales, from scientists and engineers to chefs and travelers. It ensures accurate and reliable conversions, making it a valuable tool in various scenarios.