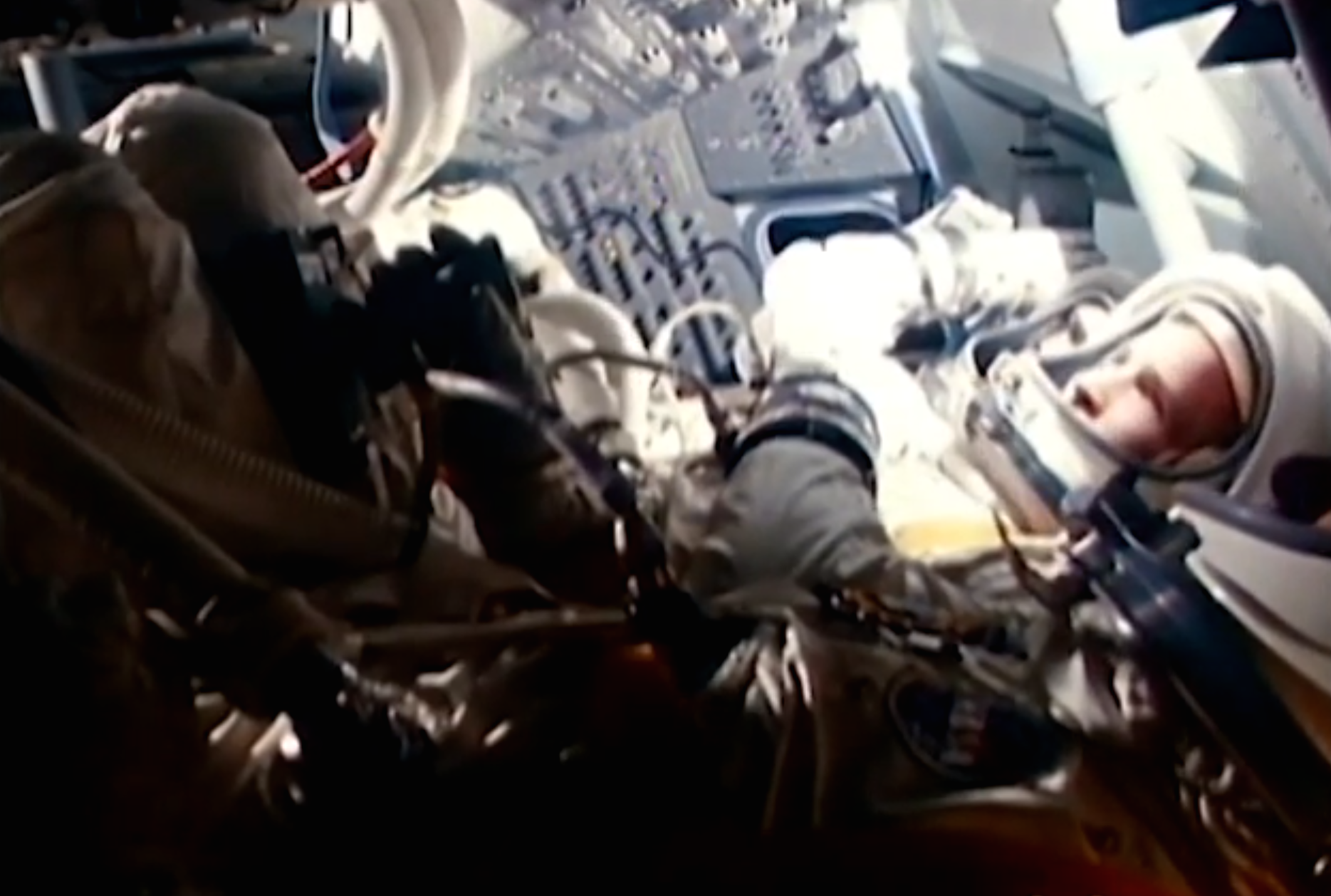
Apollo 1 marked a significant milestone in the history of space exploration, albeit for unfortunate reasons. It was the first mission in NASA's Apollo program, which aimed to land humans on the Moon and bring them safely back to Earth. Tragically, the mission never left the launch pad due to a catastrophic cabin fire during a pre-launch test. The incident resulted in the loss of three brave astronauts: Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee. This early setback became a catalyst for significant changes in spacecraft design and safety protocols, underscoring the inherent risks of venturing into space.
The Apollo 1 tragedy was a sobering reminder of the perils associated with space travel. The mission was intended to be an Earth-orbiting mission, testing the Apollo Command and Service Module (CSM) systems. However, a fire broke out in the command module during a routine "plugs-out" test on January 27, 1967. The pressurized, oxygen-rich environment inside the cabin contributed to the rapid spread of the fire, leaving the crew with no chance of survival. The incident prompted NASA to conduct an exhaustive investigation, leading to crucial changes in spacecraft design, materials, and procedures that enhanced the safety of subsequent missions.
Despite the tragic outcome, Apollo 1 served as a pivotal learning experience for NASA and the broader aerospace community. The loss of Grissom, White, and Chaffee was not in vain, as it led to the implementation of more stringent safety measures that ensured the success of future Apollo missions, ultimately culminating in the historic Apollo 11 Moon landing. This article delves into the details of Apollo 1, examining the events leading up to the tragedy, the subsequent investigation and changes, and the lasting impact on space exploration.
Read also:Interior Define A Guide To Personalized Home Furnishings And Design
Table of Contents
- Biography of Apollo 1 Astronauts
- What Led to the Apollo 1 Tragedy?
- The Design and Objectives of Apollo 1
- How Did the Apollo 1 Investigation Unfold?
- Changes in Safety Protocols After Apollo 1
- The Impact of Apollo 1 on NASA
- How Did Apollo 1 Influence Future Missions?
- Personal Details of the Apollo 1 Crew
- What Was the Public Reaction to Apollo 1?
- The Legacy of Apollo 1
- How Did Apollo 1 Change Space Exploration?
- Apollo 1 Memorials and Tributes
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Biography of Apollo 1 Astronauts
The Apollo 1 mission was manned by three experienced astronauts, each with a unique background and significant contributions to the space program. Their dedication and bravery have left a lasting legacy in the annals of space exploration.
Virgil "Gus" Grissom
Virgil "Gus" Grissom was an accomplished astronaut and one of NASA's original Mercury Seven astronauts. Born on April 3, 1926, in Mitchell, Indiana, Grissom was a decorated pilot in the United States Air Force before joining NASA. He became the second American to fly in space during the Mercury-Redstone 4 mission, known as Liberty Bell 7. Grissom's experience and leadership made him a natural choice for the Apollo 1 mission.
Edward H. White II
Edward H. White II was born on November 14, 1930, in San Antonio, Texas. He was a test pilot for the U.S. Air Force before being selected as an astronaut. White became the first American to conduct a spacewalk during the Gemini 4 mission, earning widespread acclaim for his bravery and skill. His contributions to the Gemini program made him an invaluable member of the Apollo 1 crew.
Roger B. Chaffee
Roger B. Chaffee was the youngest member of the Apollo 1 crew, born on February 15, 1935, in Grand Rapids, Michigan. Chaffee was a talented naval aviator and engineer who joined NASA in 1963. Though Apollo 1 was to be his first spaceflight, Chaffee's technical expertise and enthusiasm for the mission played a crucial role in the preparation and planning stages.
Personal Details of the Apollo 1 Crew
| Name | Birth Date | Birth Place | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgil "Gus" Grissom | April 3, 1926 | Mitchell, Indiana | Command Pilot |
| Edward H. White II | November 14, 1930 | San Antonio, Texas | Senior Pilot |
| Roger B. Chaffee | February 15, 1935 | Grand Rapids, Michigan | Pilot |
What Led to the Apollo 1 Tragedy?
The tragic events of Apollo 1 were the culmination of several contributing factors, stemming from both design flaws and procedural oversights. Understanding these elements is crucial for comprehending the full scope of the incident.
The Plugs-Out Test
The "plugs-out" test was intended to be a routine pre-flight check, simulating the spacecraft's internal systems operating independently of external power sources. This test was conducted to ensure all systems were functioning correctly before the actual launch. However, the test's conditions inadvertently set the stage for disaster.
Read also:The Dietary Habits Of Sea Turtles Do They Eat Jellyfish
Design Flaws and Material Choices
One of the primary factors that contributed to the Apollo 1 tragedy was the choice of materials used in the spacecraft's construction. The cabin was filled with flammable materials, including nylon netting and Velcro, which quickly ignited in the high-pressure, pure oxygen environment. The hatch design further exacerbated the situation, as it opened inward and required several minutes to release, trapping the crew inside during the fire.
Electrical System Malfunctions
Investigations revealed that a spark from a frayed wire or faulty connection likely ignited the fire. The spacecraft's complex electrical system contained numerous potential ignition sources, and the pure oxygen atmosphere allowed even a small spark to become catastrophic. This highlights the importance of rigorous testing and inspection of all components in spacecraft design.
The Design and Objectives of Apollo 1
Apollo 1 was designed as a critical step in NASA's ambitious goal of landing humans on the Moon. The mission's primary objectives included testing the Command and Service Module (CSM) systems and evaluating the spacecraft's performance in low Earth orbit. Despite its tragic end, understanding the design and objectives of Apollo 1 provides valuable insights into the early days of the Apollo program.
The Command and Service Module
The Apollo 1 mission featured the Command and Service Module (CSM), a crucial component of the Apollo spacecraft. The CSM consisted of two parts: the Command Module, which housed the crew and controls, and the Service Module, which contained the spacecraft's propulsion and support systems. The CSM was designed to support the crew for up to 14 days in space and was a significant advancement over previous spacecraft designs.
Mission Objectives
The primary objectives of Apollo 1 were to test the CSM systems, evaluate the spacecraft's performance in low Earth orbit, and prepare for future lunar missions. The mission was also intended to demonstrate the feasibility of long-duration spaceflights and validate the Apollo spacecraft's ability to safely transport astronauts to and from the Moon.
Pre-Launch Preparations
The Apollo 1 mission underwent extensive pre-launch preparations, including numerous tests and simulations. The crew trained rigorously for various mission scenarios, while engineers worked tirelessly to ensure the spacecraft was ready for launch. These efforts underscored the complexity and challenges associated with space exploration during this pivotal period in history.
How Did the Apollo 1 Investigation Unfold?
The Apollo 1 tragedy prompted a thorough investigation to determine the cause of the fire and prevent future incidents. The investigation's findings led to significant changes in spacecraft design and safety protocols, ultimately improving the safety of future missions.
The Apollo 204 Review Board
In the wake of the Apollo 1 tragedy, NASA established the Apollo 204 Review Board to investigate the incident's causes and recommend corrective actions. The board consisted of experts from various fields, including engineering, safety, and operations, who conducted a comprehensive examination of the spacecraft, materials, and procedures involved in the mission.
Key Findings and Recommendations
The Apollo 204 Review Board identified several critical factors that contributed to the fire, including the use of flammable materials in the cabin, the high-pressure pure oxygen environment, and the inward-opening hatch design. The board recommended numerous changes to spacecraft design and safety protocols, such as using non-flammable materials, improving cabin ventilation, and redesigning the hatch for rapid egress in emergencies.
Impact on NASA and the Aerospace Industry
The investigation's findings had far-reaching implications for NASA and the broader aerospace industry. The lessons learned from Apollo 1 led to significant improvements in spacecraft safety and design, ultimately contributing to the success of future Apollo missions. These changes also influenced safety protocols and procedures across the aerospace industry, underscoring the importance of rigorous testing and inspection in ensuring the safety of space exploration.
Changes in Safety Protocols After Apollo 1
The Apollo 1 tragedy served as a catalyst for significant changes in safety protocols and procedures within NASA and the aerospace industry. These changes were designed to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future and to ensure the safety of astronauts participating in space missions.
Material and Design Modifications
One of the most significant changes following the Apollo 1 tragedy was the modification of materials and design elements used in spacecraft construction. NASA implemented the use of non-flammable materials and improved cabin ventilation systems to reduce the risk of fire. Additionally, the hatch was redesigned to open outward, allowing for rapid egress in emergencies.
Enhanced Training and Procedures
In addition to material and design changes, NASA also enhanced training and procedures for astronauts and ground personnel. This included more rigorous simulations and emergency response drills, as well as improved communication protocols between the crew and mission control. These changes were intended to ensure that all personnel were prepared to respond effectively to potential emergencies during missions.
Long-Term Impact on Space Safety
The safety protocol changes implemented after Apollo 1 had a lasting impact on the space industry, setting new standards for spacecraft design and operations. These improvements contributed to the success of subsequent Apollo missions and continue to influence safety practices in the aerospace industry today. The lessons learned from Apollo 1 underscore the importance of prioritizing safety in the pursuit of space exploration.
The Impact of Apollo 1 on NASA
The Apollo 1 tragedy had a profound impact on NASA, shaping the agency's approach to space exploration and safety for decades to come. The incident highlighted the inherent risks of space travel and underscored the importance of rigorous testing and safety protocols in ensuring mission success.
Reevaluation of the Apollo Program
Following the Apollo 1 tragedy, NASA conducted a thorough reevaluation of the Apollo program, assessing the mission's objectives, design, and safety protocols. This reevaluation led to significant changes in spacecraft design and procedures, ultimately contributing to the success of future Apollo missions and the eventual Moon landing.
Strengthening NASA's Commitment to Safety
The Apollo 1 tragedy reinforced NASA's commitment to safety, prompting the agency to prioritize the well-being of astronauts and mission success over ambitious timelines. This shift in focus led to the development of more stringent safety protocols and procedures, ensuring that future missions were conducted with the highest standards of safety and reliability.
Legacy of the Apollo 1 Crew
The legacy of the Apollo 1 crew lives on in the lessons learned from the tragedy and the subsequent changes that improved the safety of space exploration. The bravery and dedication of Grissom, White, and Chaffee continue to inspire future generations of astronauts and engineers, serving as a reminder of the sacrifices made in the pursuit of space exploration.
How Did Apollo 1 Influence Future Missions?
The lessons learned from the Apollo 1 tragedy played a crucial role in shaping the success of future space missions, both within the Apollo program and beyond. These lessons influenced spacecraft design, safety protocols, and mission planning, ultimately contributing to the success of subsequent missions.
Improvements in Spacecraft Design
The design changes implemented after Apollo 1, including the use of non-flammable materials and the redesign of the spacecraft hatch, significantly improved the safety of future missions. These changes were instrumental in ensuring the success of the Apollo program, culminating in the historic Apollo 11 Moon landing.
Enhanced Safety Protocols
The safety protocols developed in response to the Apollo 1 tragedy have had a lasting impact on the aerospace industry, setting new standards for spacecraft design and operations. These protocols continue to influence safety practices in the industry today, ensuring that the lessons learned from Apollo 1 are applied to future missions.
Legacy of the Apollo Program
The Apollo program's success, despite the initial setback of Apollo 1, serves as a testament to the resilience and determination of NASA and the broader aerospace community. The lessons learned from Apollo 1 contributed to the program's ultimate success, paving the way for future space exploration endeavors and inspiring generations of scientists, engineers, and astronauts to pursue their dreams.
Personal Details of the Apollo 1 Crew
The Apollo 1 crew consisted of three dedicated and accomplished astronauts, each with a unique background and significant contributions to the space program. Their personal details provide insight into their lives and the legacy they left behind.
| Name | Birth Date | Birth Place | Role |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgil "Gus" Grissom | April 3, 1926 | Mitchell, Indiana | Command Pilot |
| Edward H. White II | November 14, 1930 | San Antonio, Texas | Senior Pilot |
| Roger B. Chaffee | February 15, 1935 | Grand Rapids, Michigan | Pilot |
What Was the Public Reaction to Apollo 1?
The Apollo 1 tragedy elicited a strong public reaction, as people around the world mourned the loss of the three astronauts and grappled with the implications of the incident for the future of space exploration.
National Mourning
The loss of Grissom, White, and Chaffee was met with widespread mourning across the United States and beyond. The astronauts were honored for their bravery and dedication to the pursuit of space exploration, with memorials and tributes held in their honor.
Impact on Public Perception of Space Exploration
The Apollo 1 tragedy prompted a reevaluation of the risks associated with space exploration, leading to increased scrutiny of NASA's programs and safety protocols. While the incident raised questions about the feasibility and safety of space travel, it also underscored the importance of continued investment in research and development to overcome the challenges of space exploration.
Legacy of the Apollo 1 Crew
The legacy of the Apollo 1 crew continues to inspire future generations of astronauts and engineers, serving as a reminder of the sacrifices made in the pursuit of space exploration. Their dedication and bravery have left a lasting impact on the aerospace industry, ensuring that the lessons learned from their tragic loss contribute to the success of future missions.
The Legacy of Apollo 1
The legacy of Apollo 1 is characterized by the lessons learned from the tragedy and the subsequent changes that improved the safety and success of future space missions. The incident serves as a reminder of the inherent risks of space exploration and the importance of rigorous testing and safety protocols.
Contributions to Spacecraft Safety
The changes implemented in response to the Apollo 1 tragedy, including the use of non-flammable materials and the redesign of the spacecraft hatch, have had a lasting impact on spacecraft safety. These improvements continue to influence safety practices in the aerospace industry today, ensuring that the lessons learned from Apollo 1 are applied to future missions.
Inspiration for Future Generations
The bravery and dedication of the Apollo 1 crew continue to inspire future generations of astronauts and engineers, serving as a reminder of the sacrifices made in the pursuit of space exploration. Their legacy lives on in the success of subsequent Apollo missions and the continued exploration of space by NASA and other space agencies around the world.
Enduring Impact on the Aerospace Industry
The lessons learned from Apollo 1 have had a lasting impact on the aerospace industry, setting new standards for spacecraft design and operations. These lessons continue to influence safety practices and procedures across the industry, ensuring that the legacy of Apollo 1 contributes to the success of future space exploration endeavors.
How Did Apollo 1 Change Space Exploration?
The Apollo 1 tragedy marked a turning point in the history of space exploration, leading to significant changes in spacecraft design, safety protocols, and mission planning. These changes have had a lasting impact on the aerospace industry, ensuring the safety and success of future missions.
Improvements in Spacecraft Safety
The design changes implemented after Apollo 1, including the use of non-flammable materials and the redesign of the spacecraft hatch, significantly improved the safety of future missions. These changes were instrumental in ensuring the success of the Apollo program and continue to influence safety practices in the aerospace industry today.
Enhanced Safety Protocols
The safety protocols developed in response to the Apollo 1 tragedy have set new standards for spacecraft design and operations, ensuring that the lessons learned from the incident are applied to future missions. These protocols continue to influence safety practices across the aerospace industry, underscoring the importance of rigorous testing and inspection in ensuring the safety of space exploration.
Legacy of the Apollo Program
The Apollo program's success, despite the initial setback of Apollo 1, serves as a testament to the resilience and determination of NASA and the broader aerospace community. The lessons learned from Apollo 1 contributed to the program's ultimate success, paving the way for future space exploration endeavors and inspiring generations of scientists, engineers, and astronauts to pursue their dreams.
Apollo 1 Memorials and Tributes
The legacy of the Apollo 1 crew is honored through various memorials and tributes, commemorating their bravery and dedication to the pursuit of space exploration. These memorials serve as a reminder of the sacrifices made in the pursuit of space exploration and inspire future generations to continue the quest for knowledge and discovery.
Memorials and Monuments
Numerous memorials and monuments have been established to honor the Apollo 1 crew, including the Apollo 1 Memorial at Arlington National Cemetery and the Space Mirror Memorial at the Kennedy Space Center. These sites serve as a tribute to the astronauts' bravery and dedication, ensuring that their legacy is remembered and celebrated.
Annual Remembrance Events
NASA and other organizations hold annual remembrance events to honor the Apollo 1 crew and other astronauts who have lost their lives in the pursuit of space exploration. These events serve as a reminder of the sacrifices made in the quest for knowledge and discovery, inspiring future generations to continue the pursuit of space exploration.
Legacy of the Apollo 1 Crew
The legacy of the Apollo 1 crew continues to inspire future generations of astronauts and engineers, serving as a reminder of the sacrifices made in the pursuit of space exploration. Their dedication and bravery have left a lasting impact on the aerospace industry, ensuring that the lessons learned from their tragic loss contribute to the success of future missions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What was the cause of the Apollo 1 fire?
The Apollo 1 fire was caused by a spark from a frayed wire or faulty connection, which ignited the flammable materials in the high-pressure, pure oxygen environment inside the spacecraft cabin.
2. How did NASA respond to the Apollo 1 tragedy?
In response to the Apollo 1 tragedy, NASA conducted a thorough investigation and implemented significant changes in spacecraft design, materials, and safety protocols to prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
3. What changes were made to the spacecraft design after Apollo 1?
After Apollo 1, NASA made several changes to the spacecraft design, including the use of non-flammable materials, improved cabin ventilation, and redesigning the hatch to open outward for rapid egress in emergencies.
4. How did Apollo 1 influence future space missions?
The lessons learned from Apollo 1 influenced spacecraft design, safety protocols, and mission planning, ultimately contributing to the success of subsequent Apollo missions and the continued exploration of space.
5. Who were the astronauts on the Apollo 1 mission?
The Apollo 1 mission was manned by three astronauts: Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Edward H. White II, and Roger B. Chaffee.
6. What is the legacy of the Apollo 1 crew?
The legacy of the Apollo 1 crew is characterized by their bravery and dedication to the pursuit of space exploration. Their contributions have had a lasting impact on the aerospace industry, ensuring the success of future missions.
Conclusion
The Apollo 1 tragedy serves as a somber reminder of the inherent risks associated with space exploration and the importance of rigorous testing and safety protocols. The lessons learned from the incident have had a profound and lasting impact on the aerospace industry, shaping the success of future missions and ensuring the safety of astronauts participating in space exploration endeavors. The bravery and dedication of the Apollo 1 crew continue to inspire future generations, serving as a testament to the resilience and determination of those who dare to push the boundaries of human knowledge and discovery.