The English language is a labyrinth of rules, exceptions, and fascinating complexities. Among its many intricacies, the word "is" often raises questions about its grammatical role. Is "is" a preposition? Many learners of English and even native speakers often find themselves puzzled by such queries, especially when dissecting the functional parts of speech. Understanding the proper classification of "is" not only clarifies its usage but also strengthens one’s overall command of the language.
Words like "is" are integral to the structure of English grammar, yet their roles are frequently misunderstood. While "is" may appear simple, its significance in conveying tense, linking subjects, and forming predicates is profound. The confusion often arises because "is" does not fit neatly into categories like nouns, verbs, or prepositions for some individuals. This article delves deep into the grammatical identity of "is," explaining why it is not a preposition but rather a verb—specifically, a linking verb.
This guide is crafted to provide a comprehensive understanding of "is," its function in sentences, and why it is not classified as a preposition. We’ll explore how "is" works within the broader structure of English grammar, address common misconceptions, and answer frequently asked questions. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or simply a language enthusiast, this article serves as a definitive resource for mastering the nuances of "is."
Read also:Dedham Health And Athletic Enhance Your Wellbeing With Fitness And Wellness
Table of Contents
- What Does "Is" Mean?
- Why Is "Is" Not a Preposition?
- How Is "Is" Used in Grammar?
- The Role of "Is" in Linking Verbs
- Is "Is" a Helping Verb Too?
- Examples of "Is" in Sentences
- Is "Is" Ever a Preposition?
- Common Misconceptions About "Is"
- Differences Between Verbs and Prepositions
- Why Grammar Matters
- Does "Is" Change Its Role in Questions?
- How to Teach the Role of "Is"?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Does "Is" Mean?
The word "is" stems from the verb "to be," which is one of the most fundamental verbs in the English language. It functions as a present tense, third-person singular form of "to be." This means it is used when referring to a singular subject in the present moment. For instance, in the sentence "She is happy," the word "is" connects the subject "she" with the predicate "happy."
Grammatically, "is" serves as a linking verb, which means it does not show action but rather links the subject of the sentence to additional information about the subject. It can also indicate existence or state-of-being. For example:
- "He is a teacher." (Linking subject with predicate noun)
- "The sky is blue." (Linking subject with predicate adjective)
- "There is a book on the table." (Indicating existence)
Its role is crucial in sentence construction, as it helps establish a relationship between the subject and the rest of the sentence. Despite its simplicity, "is" plays a pivotal role in forming complete and meaningful sentences.
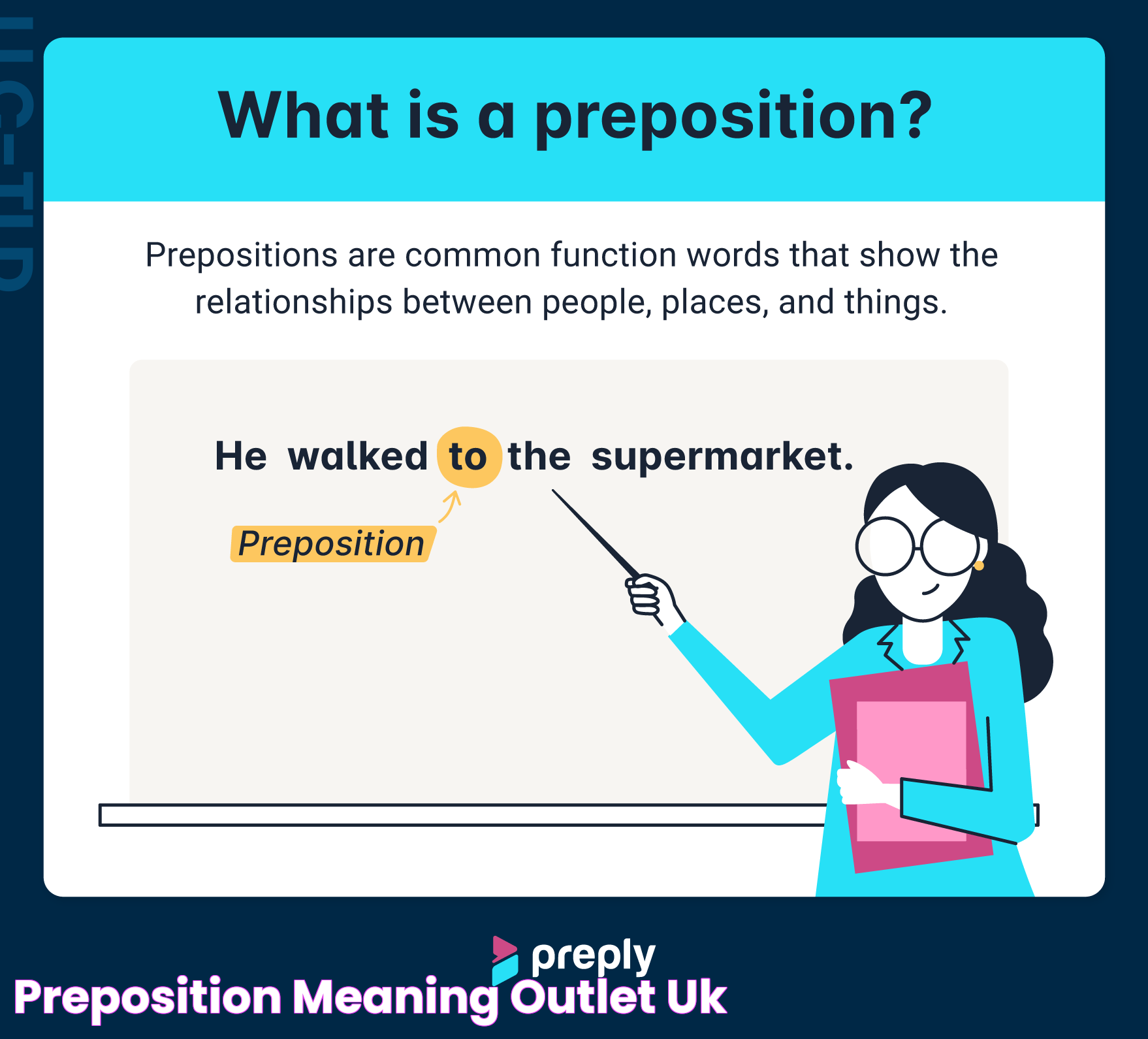
Why Is "Is" Not a Preposition?
Many people mistakenly classify "is" as a preposition, but this is not accurate. Prepositions are words that show relationships between nouns (or pronouns) and other words in a sentence, often indicating direction, place, time, or cause. Examples of prepositions include "in," "on," "at," and "by."
In contrast, "is" is a verb. Here’s why "is" cannot be a preposition:
- Function: Prepositions provide relational context, while "is" serves as a linking verb that connects the subject to the predicate.
- Placement: Prepositions are typically followed by objects, whereas "is" is followed by predicates (either nouns, pronouns, or adjectives).
- Purpose: The purpose of "is" is to establish a state of being or existence, not to indicate relationships between words.
For instance, in the sentence "The apple is red," the word "is" connects the subject "apple" to its description "red." A preposition, in this context, would function differently, such as "The apple is on the table," where "on" indicates the position of the apple.
Read also:All You Need To Know About The Name In Japanese A Cultural Insight
How Is "Is" Used in Grammar?
The usage of "is" in grammar is vast and varied. Primarily, it functions as a linking verb, but it also appears in auxiliary roles. Below is a breakdown of its primary grammatical functions:
1. Linking Verb
As a linking verb, "is" connects the subject to a complement, which can be a noun, pronoun, or adjective. For example:
- "She is an artist." (Linking subject to predicate noun)
- "The weather is cold." (Linking subject to predicate adjective)
2. Indicating Existence
In some cases, "is" is used to indicate existence. For example:
- "There is a problem with the system."
- "Is there anyone home?"
3. Forming Questions
"Is" is frequently used to form questions in English. For example:
- "Is she coming to the party?"
- "What is the time?"
The Role of "Is" in Linking Verbs
Linking verbs are essential in English, and "is" is one of the most commonly used among them. Linking verbs do not show action; instead, they link the subject of the sentence to information about the subject. For example:
- "The light is bright." (Subject linked to an adjective)
- "My sister is a doctor." (Subject linked to a noun)
Understanding the role of "is" as a linking verb helps avoid confusion when analyzing sentence structures. It’s worth noting that linking verbs like "is" are often followed by complements rather than objects.
Is "Is" a Helping Verb Too?
Yes, "is" can also function as a helping (or auxiliary) verb in certain contexts. Helping verbs assist the main verb in a sentence to express tense, mood, or voice. For example:
- "She is running a marathon." (Helping verb "is" combined with the main verb "running" to indicate present continuous tense)
- "The cake is being baked." (Helping verb "is" combined with "being" to form the passive voice)
In such cases, "is" works in tandem with other verbs to provide additional grammatical information.
Examples of "Is" in Sentences
To better understand the versatility of "is," let’s examine a variety of sentence examples:
- "She is happy." (Linking verb with an adjective complement)
- "The book is on the table." (Linking verb with a prepositional phrase)
- "Is this your pen?" (Verb used in a question)
- "The car is being repaired." (Helping verb in passive voice)
- "There is a dog in the yard." (Indicating existence)
Is "Is" Ever a Preposition?
No, "is" is never classified as a preposition. While it may share certain sentence positions with prepositions, its function is entirely different. Prepositions require objects, whereas "is" connects subjects to complements.
For example:
- "The dog is in the yard." ("In" is the preposition, "is" is the linking verb)
- "She is tired." ("Is" links the subject and predicate adjective)
Common Misconceptions About "Is"
Many misconceptions surround the word "is," often leading to confusion. Here are some of the most common:
- Confusing "is" with prepositions due to its position in sentences.
- Misinterpreting "is" as a standalone verb in passive constructions.
- Assuming "is" always indicates present tense without considering context.
Clarifying these misconceptions is crucial for accurate grammatical analysis.
Differences Between Verbs and Prepositions
To firmly establish why "is" is not a preposition, it’s helpful to compare the two:
- Verbs: Indicate action or state of being. Example: "She is happy."
- Prepositions: Indicate relationships between words. Example: "The book is on the table."
This distinction is key to understanding the grammatical role of "is."
Why Grammar Matters
Grammar is the foundation of effective communication. Understanding the roles of words like "is" ensures clarity and precision in both written and spoken English. It also helps avoid common errors and enhances overall language proficiency.
Does "Is" Change Its Role in Questions?
No, "is" retains its role as a linking verb or auxiliary verb even in questions. Its placement may change, but its function remains consistent. For example:
- Statement: "She is happy."
- Question: "Is she happy?"
How to Teach the Role of "Is"?
Teaching the role of "is" can be simplified by using real-life examples, visual aids, and interactive exercises. Focus on its function as a linking verb and auxiliary verb, and contrast it with prepositions to clarify its unique role in grammar.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is "is" the same as "are"?
No, "is" and "are" are both forms of the verb "to be," but "is" is used for singular subjects, while "are" is used for plural subjects.
2. Can "is" ever be used as a noun?
In rare cases, "is" can be used as a noun in philosophical or linguistic contexts, referring to the concept of existence or being.
3. Why do people confuse "is" with prepositions?
Confusion often arises due to the placement of "is" in sentences, which can be similar to prepositions. However, their functions are entirely different.
4. Does "is" indicate tense?
Yes, "is" indicates present tense when used as a verb.
5. How can I identify "is" in a sentence?
Look for its role in linking the subject to a complement or assisting a main verb in forming tense, mood, or voice.
6. What are some common mistakes with "is"?
Common mistakes include overusing "is" in passive constructions and misclassifying it as a preposition.
Conclusion
In summary, "is" is not a preposition but a versatile linking and helping verb that plays a critical role in English grammar. Understanding its function enhances clarity and fluency in communication. By distinguishing it from prepositions and other parts of speech, learners can master its usage and avoid common pitfalls. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently navigate the complexities of English grammar and ensure accurate, effective communication.